Thursday, June 24, 2010
Week 12
Monday, June 21, 2010
Week 11
Monday, June 14, 2010
Week 10
Call Routing Strategies
- Lowest total talk time
- Last agent
- Fewest received calls
- Round Robins
Thursday, June 10, 2010
Week 9
Saturday, June 5, 2010
Week 8
Week 7
Nuance
IBM
LumenVox
Amcom software
Fonix
CMU Sphinx
MacSpeech
SRC
Sensory
Philips
eON Communication
Stratasoft
Vertical Networks
APEX Voice Communications
Avaya
Cantata (Dialogic website)
ClickFox
Spoken
Prosodie
Convergys
Eagle ACD
Angel.com
Five9
Cincom
UCN
Envox Worldwide
Kunnect
Packet8
TeleTech
Virtual PBX
Sunday, May 30, 2010
Week 6
Speech recognition (also known as automatic speech recognition or computer speech recognition) converts spoken words to text. The term "voice recognition" is sometimes used to refer to recognition systems that must be trained to a particular speaker—as is the case for most desktop recognition software. Recognizing the speaker can simplify the task of translating speech. Speech recognition applications include voice dialing (e.g., "Call home"), call routing (e.g., "I would like to make a collect call"), dogmatic appliance control, search (e.g., find a podcast where particular words were spoken), simple data entry (e.g., entering a credit card number), preparation of structured documents (e.g., a radiology report), speech-to-text processing (e.g., word processors or emails), and aircraft (usually termed Direct Voice Input).
Monday, May 17, 2010
Week 5
Call Queuing
Call Queuing is a sophisticated queuing system that allows to accept more calls into the telephone system than have extensions or employees capable of answering them.It allows dealing efficiently with calling peaks without losing valued customer’s calls and projects a professional image of business. With Call Queuing, instead of getting an engaged tone the customers are answered automatically and held in a queue. While they are waiting for a representative they receive personal messages about how many calls are in front of them followed by music while they are waiting

ACD
In telephony, an Automatic Call Distributor (ACD), also known as Automated Call Distribution, is a device or system that distributes incoming calls to a specific group of terminals that agents use. It is often part of a computer telephony integration (CTI) system. Routing incoming calls is the task of the ACD system. ACD systems are often found in offices that handle large volumes of incoming phone calls from callers who have no need to talk to a specific person but who require assistance from any of multiple persons (e.g., customer service representatives) at the earliest opportunity.
 After doing all these research, I did some practical testing about call queuing. Here are the steps:
After doing all these research, I did some practical testing about call queuing. Here are the steps:
Step 1: Agent login
Example: An agent in the telemarketing queue picks up the phone and dials #9000. The agent hears an invalid login message and is asked for his/her name and password. The auditing queue follows the same procedure.
Step 2: Queue
Once in the queue, the agent will hear MOH if defined. When a call comes in the telemarketing queue, the agent will hear a “beep” and will be connected to that call.
Step 3: Call ending
When the agent finishes the call, he/she can:
• Press ‘*’ to disconnect and stay in the queue.
• Disconnect the phone, disconnecting to the queue.
• Press #8000 to transfer the call for auditing.
Week 4
- Create subscriber account in asterisk
- Register the subscriber account in Zoiper
- Edit ring group in asterisk. (If want to use find me choose ring all if is follow me choose ring in order.)
- Testing Find Me/ follow me
- Registered the extension that wanted to put in 3-party conference.
- Create a conference bridge in asterisk
- Call the conference bridge
- Enter the conference
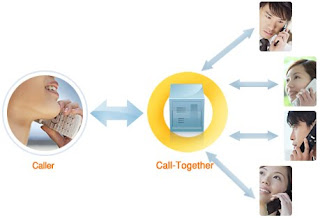
Week 3

Find Me, Follow Me

3-party Conferencing

Sunday, April 18, 2010
Week 2


 15 April 2010:
15 April 2010:.jpg)
Saturday, April 10, 2010
Week 1

7/4/2010:

AsteriskNOW makes it easy to create custom telephony solutions by automatically installing the "plumbing". Much of the complexity of Asterisk and Linux is handled by the installer and the administrative GUI. Application developers and intergrators can concentrate on building their solution. AsteriskNOW was built for application developers, systems integrators, students, hackers and others who want to create custom solutions with Asterisk.


Wednesday, April 7, 2010
1st day of my industrial training
Time : 10 am - 7 pm
Venue : DARE BPO SDN BHD
Plug and Play Technology Garden
Suite 7.01, level 7, The Gardens South Tower, Mid valley City
Lingkaran Syed Putra 59200 Kuala Lumpur
Today is my first day of industrial training, early morning around 8.30am I went to take ktm to go to my office which is mid valley..

The Gardens lobby
At 9.45am I already reach Gardens lobby to meet my friends and my supervisor Mr Jeffrey. After that, he bring us go to the office.

This is the place we going to spent for 3 months
Mr Jeffrey introduce us the product of the company and what our job scope for this 3 months. Basically our company is more on IT and Telecommunication. We created the program easier for the customer to receive their message, fax and email. For example, the person can set his/her cell phone, office, and house number to our program and if someone call he/she this 3 phone will ring at the same time and once he/she picks up one of it the others two will automatic turn off.

This is our company product

We are trying to use the product
This is my first day of work, just everything fine.



















.jpg)